The Metaverse – Why it is more than hype
How business evolves in the virtual reality
With the metaverse, we are facing a shift that will change business models just as much as the Internet has in recent decades. Anyone who dismisses it as hype for gamers and nerds is closing their eyes to the advantages of early participation.
Since Mark Zuckerberg announced his Metaverse mission, it has become hype. If Zuckerberg has his way, large parts of our social life will soon take place in the Metaverse. Since this future is very likely in view of the rapidly evolving technological developments, especially in the fields of artificial intelligence and virtual reality, it is worth taking a look at what lies ahead of us.
Index
What exactly is the Metaverse?
What exactly will be behind Zuckerberg’s “The Metaverse” in particular, we will certainly find out in the near future. There is no clear definition for the metaverse in general. It can be compared to the early days of the Internet, where there was also no clear idea of what we perceive as the Internet today. Generally speaking, the metaverse is understood as a virtual world, which on the one hand is technologically characterized by virtual reality and augmented reality and exists independently of individual users. Unlike a classic (virtual reality) game, which I start and finish, the existence of the virtual world is permanent and individuals enter and leave it to participate. Today, platforms such as Roblox and Fortnite, which have gaming at their origin, are counted as metaverses.
Economy in the metaverse
In addition to the social aspects, the metaverse is characterized by a digital economy. This is precisely why it has become so interesting for brands like Adidas, Nike, Gucci and Balenciaga in recent months. This is about far more than opening up new advertising opportunities and sales channels for their own physical products. Completely new markets for native digital products are already emerging in the metaverse, which the big brands want to occupy. If they fail to do so, they will be threatened by digital-native brands that hardly anyone outside the bubble is aware of today. What may seem like a bad joke to many has the potential to become the new top brand. We are talking about NFTs like BoredApe and CloneX. First in the headlines in view of the seemingly horrendous sales sums of NFTs, they quickly developed into the status symbol of the crypto community and are now stepping up to become a brand themselves. May it be rational or irrational motives that lead to these developments. They are all based on human behavior that has been known for a long time. The only difference to the development of traditional brands is that the digitally native emergence of brands is significantly accelerated, even disruptive. To understand why the positioning of the brand in the metaverse makes a lasting contribution to the business model, I recommend my article “Crypto Assets – A social capital game“. The natively digital supply chain also offers the opportunity for the so-called Creator Economy. By removing hurdles on both the production and marketing sides, creators can for the first time interact and transact directly with consumers. Through NFT and tokenization, copyrights and ownership rights can be digitally fixed so that digital business models can be natively mapped onto them without the need for the mediator in the physical world that is required today.
Relevance beyond Art & Gaming
So is the metaverse only relevant for companies in the gaming, art and consumer goods sectors? At the latest with the commitment of companies like Microsoft to the Metaverse, it should be clear: Not at all! Just as the Internet is a basic infrastructure for all businesses today, so will the Metaverse be in the future. Some examples of this:
Before the pandemic, face-to-face meetings were commonplace. I, as well, sometimes traveled all day to attend a 1-hour meeting. Fortunately, that has changed radically. Today, remote digital collaboration is commonplace. Still, video conferencing collaboration is not yet completely comparable to a physical meeting. VR and AR technology will significantly improve the user experience of online meetings. But more than that, in the business metaverse we will be able to collaborate with colleagues globally as if we were sitting locally in an office. The physical company headquarters and “the office” will no longer play a major role.
Working in global teams will become a matter of course in the metaverse, even for smaller companies. The traditional employee relationship will also change. What we are already seeing in the Creator Economy will continue. Traditional ties to one employer will gradually be replaced by competence networks in which professionals organize themselves to perform work in various projects. In recruiting, the digital business self, i.e., the employee’s track record, will play a leading role. Companies that can recruit in the virtual space and integrate employees into virtual teams will gain significant market advantages.
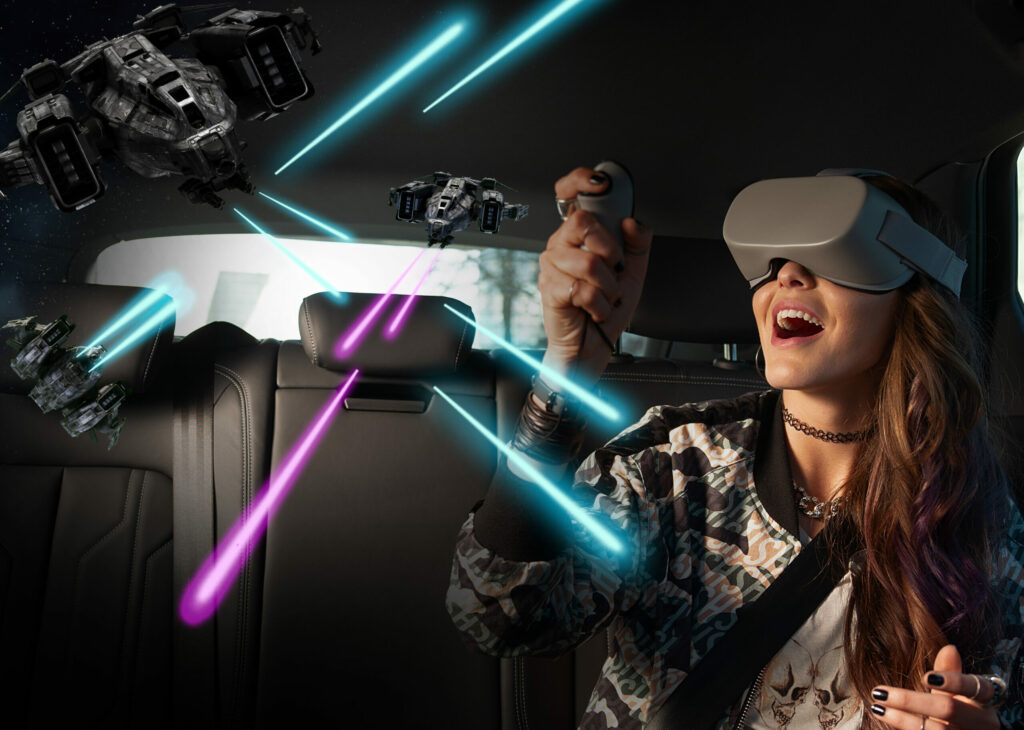
Existing business models will also change. Let’s look at the automotive industry, for example. Here, work is being done on concepts for linking virtual worlds with mobility. Companies like Holoride are already addressing this market today.

Metaverse – The next evolutionary stage of the Internet?
Is the Metaverse simply a further development of the existing Internet? Unfortunately, this question must be answered with YES and NO. The Internet in its origin is planned as a network, which enables an open exchange of data and thus a decentralized growth through interoperability of the protocol level. The metaverse in the spirit of Zuckerberg is rather a continuation of the social networks, which are already today attacking the privacy and data autonomy of the users. The metaverse extends the idea of social networks to almost all areas of life. An individual’s participation in a permanently existing metaverse is associated with the emergence of a comprehensive digital self. If one leaves a digital footprint on the Internet through one’s behavior, one’s digital personality is created in the metaverse. Even though one can be anything in Zuckerberg’s metaverse vision, everything is controlled by a private company. The freedom to choose the skin color of one’s avatar does not mean sovereignty over his or her own data. Such an understanding of the Metaverse is therefore already no further development of the Internet idea, since here open protocols and interoperability are replaced by closed systems that control the digital self, i.e. the identity of the user. Openness is only created for commercial purposes. If the metaverse is understood and implemented in this way, then it can be seen as a threatening continuation of social media, which can lead to a dilemma for fundamental human rights.
Efforts to create an open metaverse based on the fundamental principles of the Internet represent an alternative to this dystopian development. The basis for this is the Web3.0 movement with decentralized approaches to digital identities, transactions and the digitization of property.

Comments are closed.