Economic Bubbles and Financial Bubbles explained – Definition, Types and 5 Stages
What are Economic Bubbles, and why should we better understand the dynamics?
Economic bubbles have been around for ages. But, what are Economic Bubbles, what types of bubbles are possible, and what stages can be observed over and over again?
Throughout history, some basic human principles have brought us to several turning-points in our economy. Constantly the perceived value, the price someone is willing to pay for something, by far outgrows the real intrinsic value of a good. This is usually short after the fall and an economic crisis leading to recession and depression.
Even famous Keynes once mentioned that economic cycles are unavoidable and “spontaneous optimism” is a bigger driver than mathematical rules for the economy in many ways. There might be many factors leading to Economic Bubbles, and we will explain the most common types and the usual stages of these financial bubbles.
Index
What is an Economic Bubble?
An economic bubble is a situation in the economy where perceived asset prices and valuations are much higher than the underlying value. The news of price increases lead to an increased spur of new investors which drive prices and amplifying the stories by new success stories until the market value and prices of assets are rapidly escalating. The steep price rise is then followed by a steep decrease/contraction as the bubble is bursting.
The effects of the bubble is usually only observed after it happened, and so it was also the case for the first known economic bubble. The Tulip mania, which led to a steep incline in prices for tulips and a surge in speculations, which then to a giant crash the year after.
Today there is another type of bubble possible, the Leveraged Bubble, which is fueled by outstanding credit. With leveraging, people lend money and speculate on assets, which lead to a leveraged effect of the own capital. Leveraged bubbles are a greater danger to the economy as they have more far-reaching effects on the whole financial industry and not just on the speculation bubble itself.
4 Types of Economic Bubbles
Generally, every type of financial asset can be involved in a bubble. But we can differentiate 4 different types, which we learned from the past.
Stock Market Bubble
A well-known stock market bubble was the famous dotcom bubble in the late 1990s. This economic bubble type involves especially equity like stocks, EFTs and other financial assets linked to companies. Usually, it is limited to a certain sector (e.g. Internet industry in the dotcom bubble) and often it is fueled by a new technology paradigm or a hyped new business model.
Asset Market Bubble
Other, outside the equities market, assets can also form an economic bubble. Asset market bubbles can be seen in real estate markets but also in currencies. In this bubble category can be also traditional currencies like EUR, USD but also new currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin and other cryptocurrencies but also NFTs.
Credit Market Bubble
When the market for business and consumer loans, dept instruments and other forms of credit is suddenly surging, then we speak of a credit market bubble. This could be corporate bonds, government issued bonds, mortgages but also an increase in leasing and “buy-now pay-later” loans.
Commodity Bubble
In commodity bubbles, the prices of traded commodities are increasing. Commodities include tangible assets and raw materials like oil, gas, gold, industrial metals, agricultural crops but also tulips like in the tulip mania.
The psychology and theories behind Economic Bubbles
There are many psychological factors that lead to the build of a bubble, and many are still not know. Many theories are also based on human behaviors that we could observe. Here is a list of the most prevalent problems we see when dealing with behavioral finance and theories of why economic bubbles can even exist.
- Herd mentality – As humans, we always want to follow the crowd, especially if we hope for a positive expected outcome.
- Short-term thinking – All other aspects are shut out as long as the investor thinks that he can “beat the market”. This also increases the likelihood of high risk-taking investment decisions.
- Hindsight Bias – Investors often justify their decisions based on one or two successful examples in the industry or from history (e.g. Amazon, Bitcoin) while little attention is given to failed investments (e.g. pets.com or many other cryptocurrencies).
- Confirmation Bias & Cognitive dissonance – Humans tend to only hear what they want to hear. Therefore, we surround ourselves with opinions, persons and publications that validate ourselves and our choices. This also stays true for companies – as long as the peers also make it this way, it is ok.
- Overconfidence & “Illusory Superiority” – When we win, it’s talent and when we lose, it’s bad luck. This phenomenon is called illusory superiority and it comes when people have success in a certain topic. The more success they have, the more they attribute it to their own talent and disregard everything else as simply bad luck. This leads to high risk-taking profiles and is also observed when gambling.
- Fear-of-missing-out (FOMO) – The fear of missing something that could make a life better is a big driver of first investors. They hear stories in the market and FOMO is responsible for a big part of the 2nd phase of a bubble – the “Boom” where many new market participants enter the market in the hope for a better future and great returns.
- Greater fool theory – This theory describes aspects of a late-stage bubble. Where people pay huge sums for already overvalued assets and believe that they will find a “greater fool” who will buy it for even more money.
5 Stages of Economic Bubbles
Usually Bubbles can only be observed after they happened, as there are not always clear signs of them visible. But there is strong evidence that almost every bubble was going through the same stages. The Economist Hyman P. Minsky was the first one to outline these 5 stages, and so we will explain them in a little more detail.
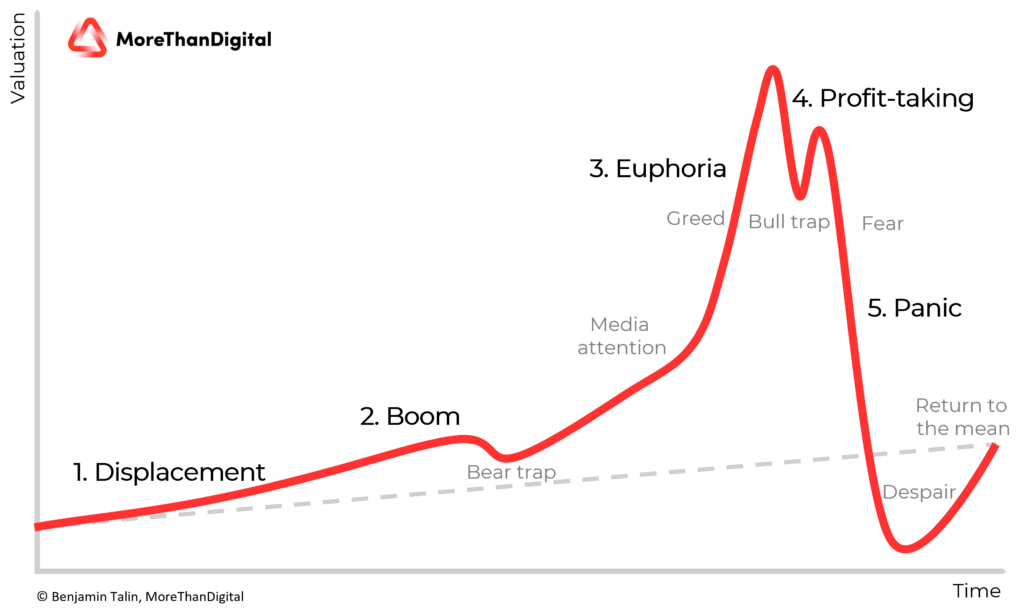
1. Displacement
Displacement happens, when investors think that a new economic paradigm occurs. This can happen with new technologies, but also with other paradigm shifts, like low interest rates and large amounts of liquidity in the market.
2. Boom
Following the Displacement, where the markets slowly adapt and slowly rise, the Boom-phase comes. This is when a lot of new entrants enter the market and participate in the investment. The widespread media coverage, large attention and also large promises lead to the so-called Fear-Of-Missing-Out (FOMO). This fear of missing a lifetime opportunity drives numerous people into the market purely for speculation.
3. Euphoria
In the euphoria phase, we see the prices skyrocket. The valuations of companies and assets can be manyfold of their real value. Often also new kind of KPIs and measures are introduced to somehow justify that this value must be real. Especially in the euphoria phase, most investors think that they will find someone else who is buying the asset for a bigger price, letting them believe that there is no limit. This theory linked to that phenomenon is called “Greater-Fool”-theory.
4. Profit-Taking
Institutional investors get the warning signs usually earlier, and therefore they start the 4th phase of the bubbly – the profit-taking and securing of the profits. Due to the irrational behaviors in the market, it can also be that large investors take out the profits too early and need to hold on to the assets for too long, diminishing the first effects, as it is always hard to predict what over-valuation is still ok and when the bubble will burst. This part will also lead to less trading and more supply on the market.
5. Panic
Once an event triggers the last stage, there is no turning back from the bubble bursting. It can be a single event; a single company crash, or some external factors that finally trigger the bubble. Asset prices fall, margin calls for investors force them to sell, and other factors including fear of losing money led to panic like sales of the assets. This leads to an excessive supply in the market for limited demand, which results in steep declines of asset prices and values as there is no “greater-fool” that would buy the asset for an overvalued price.
Economic Bubble Summary
With many kinds of economic bubbles in history, we see that there is always a potential for growing a bubble due to our nature. Behavioral economics shows that we follow the herd, we only look at information we like, and we tend to oversee facts because we are gamers by nature.
This will lead also in future to many more economic bubbles which will spur interest from a new technology, new paradigm and finally lead to a new economic cycle which starts after the contraction after a bubble. We will see what bubble will form in the future, and most likely we will only see it coming when it is too late. Especially with leveraged bubbles we will see even bigger impacts on our economy, not just for the specific niche the bubble was built in as the (financial) economy is more interwoven and interdependent globally. We should also not forget that fast spreading media news, social media filter bubbles and increasingly more extremist society, we will have a lot of amplifiers what will help spur new bubbles.

Comments are closed.