9 government policies for stimulating economic growth
What are the most efficient policies to grow an economy and support economic growth?
What can governments do to stimulate economic growth? Different demand-side and supply-side policies have their advantages and disadvantages, and we will highlight the 9 most effective policies for stimulating the economy.
After COVID, inflation, supply chain crises and more – governments around the world are looking for ways to stimulate economic growth to combat the looming recession. While there are many government policies that can be used to stimulate economic growth, this is a difficult task as there are many interdependencies and pros and cons of each policy that need to be considered. Some measures can boost economic growth in the short term, but they also have massive long-term effects, and many governments are also working against each other in the race for economic growth.
Managing the economy is also one of the most important tasks of governments, and especially in times of crisis it is more important than ever.
Index
Different policies to stimulate economic growth
There are two main types of economic policies that can be used to promote growth: demand-side policies and supply-side policies. Demand-side policies focus on increasing aggregate demand in the economy, while supply-side policies aim to increase the productive capacity of the economy.
Demand-side policies are typically implemented through fiscal policy, which is the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. For example, a government might cut taxes to boost consumer spending or increase infrastructure spending to create jobs. Supply-side policies, on the other hand, are usually implemented through monetary policy, which is the use of interest rates and the money supply to influence the economy. For example, a central bank could cut interest rates to encourage investment or print more money to increase the money supply.
Both demand-side and supply-side policies can be effective in stimulating economic growth. However, each type of policy has its own strengths and weaknesses. Demand-side policies are often criticised for being too expansionary and leading to inflationary pressures, while supply-side policies are often criticised for being too contractionary and leading to recessionary conditions. There is no single recipe for success, as many of the factors are beyond the control of governments alone.
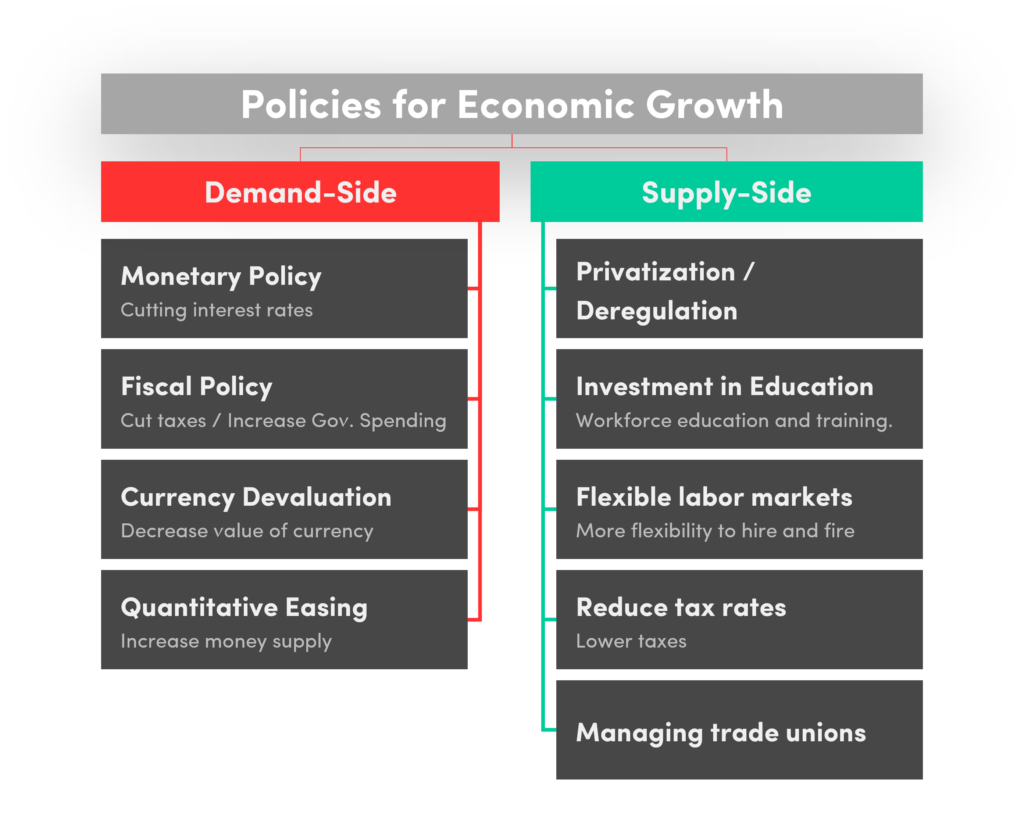
Demand-side policies
Monetary policies
There are a number of monetary policies that can be used to stimulate economic growth. One common approach is to lower interest rates, which makes it cheaper for companies to borrow money to invest. This can lead to an increase in output and employment, as well as higher wages. Another policy is quantitative easing, where the central bank buys financial assets from commercial banks to increase the amount of money in circulation. This can also lead to increased lending and investment, and therefore increased economic activity. There are pros and cons to both approaches, and the most effective policy will depend on the specific circumstances of the economy. However, monetary policy can be a powerful tool for promoting economic growth.
Fiscal policy
To achieve economic growth, a government must carefully manage its fiscal policy. This includes both taxation and spending. Too much taxation can stifle economic activity, while too much government spending can lead to inflation. The key is to strike a balance between the two. The government must also ensure that its debt is sustainable. Too much debt can put a strain on public finances and lead to higher interest rates. As a result, the government must manage its fiscal policy carefully in order to promote economic growth.
Currency devaluation
Devaluation is the deliberate downward adjustment of a currency’s exchange rate against other currencies. Devaluation often occurs when a country’s currency becomes overvalued, meaning its exchange rate is higher than what is considered fair value. When this happens, the country’s exports become more expensive and its imports become cheaper. As a result, the country’s trade balance deteriorates and its economy slows down. To revive its economy, the country may decide to devalue its currency. This makes its exports more competitive and its imports more expensive. This can help to improve the country’s trade balance and stimulate economic growth.
Quantitative easing
Quantitative easing is a monetary policy tool that can be used to stimulate economic growth. It involves the central bank creating new money and using it to buy financial assets, such as government bonds. This action lowers interest rates and increases the money supply, which can help to stimulate economic activity. Quantitative easing can also be used to target specific sectors of the economy, such as housing or infrastructure. By increasing the amount of money available for lending, quantitative easing can help to stimulate investment and economic growth. However, it is important to note that quantitative easing is not without risk and should be used carefully to avoid inflationary pressures.
Supply side policies
Privatisation & Deregulation
Every economist knows that one of the key drivers of economic growth is competition. When companies are forced to compete for market share, they are incentivised to innovate and improve their products and services. This in turn leads to greater efficiency and productivity, which drives down costs and raises living standards. One way to encourage competition is through privatisation and deregulation. Privatisation occurs when the government sells state-owned assets to private companies. This can help increase competition by opening up new markets and increasing the number of players in an industry. Deregulation, on the other hand, involves reducing government regulations on businesses. This can also help to increase competition by making it easier for new firms to enter markets and forcing existing firms to become more efficient. Both privatisation and deregulation can be controversial, but there is no denying that they can be effective tools for promoting economic growth.
Investing in education and training
A well-educated workforce is essential for any economy to compete in the global marketplace. A recent study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development found that, on average, each additional year of schooling can increase an individual’s earnings by 10%. The study also found that investment in education has a multiplier effect, generating even more economic growth. This is because educated workers are more productive, more innovative and more likely to start their own businesses. In addition, educated workers are more likely to be employed in higher-paying jobs, which boosts consumer spending and helps create jobs for others. As this research shows, investing in education is an effective way of boosting economic growth.
Flexible labour markets
A well-functioning labour market is key to a healthy economy. It helps to ensure that workers are able to find jobs that match their skills and abilities, and that firms are able to fill vacancies in a timely and efficient manner. A flexible labour market is one where there are few restrictions on hiring and firing, and where wages can rise and fall in response to changes in demand. This type of market is often seen as more responsive to the needs of firms and more efficient in matching workers to vacancies. As a result, many economists argue that a flexible labour market is essential for economic growth. While it is true that a rigid labour market can act as a barrier to growth, it is also important to remember that too much flexibility can lead to instability and insecurity. The key is to get the balance right.
Reducing tax rates
Lowering tax rates is often touted as a way to stimulate economic growth. The logic is that lower taxes mean more money in people’s pockets, which they will then spend on goods and services, boosting demand and increasing output. There is some evidence that this can work in the short term, but it is less clear whether it leads to sustained economic growth. One problem is that tax cuts tend to benefit the wealthiest people most, who are less likely to spend their extra money. Another problem is that government revenues from taxes fund important public investments, such as infrastructure and education, which can boost long-term economic growth. So while lower taxes can provide a short-term boost to the economy, there are risks in making them a central part of economic policy.
Managing union power
In recent years there has been a growing movement to reduce the power of trade unions. The argument is that unions set an artificial floor for wages, reducing the incentives for firms to invest in productivity-enhancing technologies. This ultimately leads to slower economic growth and higher unemployment. There is some evidence to support this view. For example, studies have shown that unionisation tends to reduce productivity at the firm level. It should be noted, however, that these studies tend to focus on the manufacturing sector, which is characterised by declining unionisation rates and declining relative wages. In other sectors of the economy, such as services, unions have actually been associated with higher productivity growth. In addition, research on the labour market effects of union decline has been inconclusive. Some studies find that unions have a small negative effect on employment, while others find no significant effect. In light of this evidence, it is clear that the effects of reducing union power on economic growth are far from clear. Reducing union power may lead to some short-term economic gains, but it could also have negative long-term consequences. More research is therefore needed to assess the costs and benefits of this policy before firm conclusions can be drawn.
Economic growth through other fiscal and regulatory areas
There are many ways to promote economic growth, of which the monetary policies mentioned are just a few. Factors such as population growth, productivity gains and technological innovation can all contribute to economic expansion. In addition, the ease of doing business, managing immigration and infrastructure are other smart ways to enable economic growth.
Improving infrastructure
A well-functioning infrastructure is essential for economic growth. It enables the movement of goods and people and provides the services that businesses need to operate efficiently. In many countries, however, infrastructure is in a state of disrepair. Roads are potholed and poorly lit, bridges are crumbling and power lines are outdated. This not only makes it difficult for businesses to operate, but also deters investment and slows economic growth. Countries that have made significant investments in their infrastructure have seen a corresponding increase in economic activity. To compete in the global economy, it is essential that countries have modern and efficient infrastructure.
Encourage innovation
Innovation is essential for any economy to grow and prosper. By definition, innovation is the application of new ideas or methods, and it is this process of creating new value that drives economic growth. To encourage innovation, governments and businesses need to create an environment conducive to creativity and risk-taking. This can be done by investing in research and development, encouraging entrepreneurship and removing barriers to entry. By fostering innovation, economies can unlock new sources of growth and improve the living standards of their citizens.
Encouraging the unemployed to volunteer
The unemployed often face a difficult dilemma: they need experience to get a job, but they can’t get a job without experience. As a result, many become trapped in a cycle of unemployment. One way to break this cycle is to require the unemployed to volunteer their time in exchange for economic growth. This would give them the opportunity to gain valuable work experience while helping to improve the community. It would also allow businesses to tap into a new pool of potential employees. Ultimately, this policy would benefit both the unemployed and the economy as a whole.
“Ease of doing business”
One way to promote economic growth is to remove obstacles that make it difficult to do business. This can include cutting red tape, streamlining regulations and improving access to finance. When businesses are able to operate more efficiently, they can increase output and create jobs. Another way to promote economic growth is to increase competition in the market. This can be done by removing barriers to entry for new firms and by making it easier for consumers to switch suppliers. By increasing competition, firms are forced to innovate and become more efficient in order to survive. Both of these strategies can help promote economic growth and improve the living standards of a country’s citizens.
Immigration & talent attraction
In today’s global economy, it is increasingly important for countries to attract top talent from around the world. One way to do this is to make it easier for highly skilled workers to immigrate. By making it easier for these workers to get visas and move to the country, they are more likely to choose to work there. This can help boost the country’s economy by bringing in new ideas and skills. It can also help create jobs for local people by increasing demand for goods and services. Facilitating immigration can therefore be an important tool for economic growth. It is also used internationally and can lead to a race to the bottom as governments try to attract talent with low or no taxes or other initiatives. As governments increasingly become “service providers”, highly skilled professionals can choose their government service provider by relocating.
Investing in economic resilience
Economic resilience refers to the ability of an economy to withstand, adapt to and recover from shocks such as financial crises, natural disasters or major geopolitical changes. Resilience is not just about short-term recovery, but also about the ability to emerge stronger and more sustainable in the long term. A resilient economy also limits the chances of an overall recession or even economic depression, and leads to a more stable business environment that attracts more businesses. (e.g. a key selling point for Switzerland, Singapore, etc.)
Key aspects of economic resilience include
- Diversification: Economies that rely on a small number of sectors or markets are more vulnerable to shocks. Diversification, both in terms of industrial sectors and export markets, can spread risk and reduce the impact of sectoral downturns.
- A flexible and skilled labour force: A labour market characterised by high levels of skills and adaptability can more easily shift to new opportunities or industries, minimising the impact of job losses in declining sectors. Continued investment in education and training is essential to develop such a workforce.
- Sound financial systems: Financial resilience is crucial to absorb shocks. This includes maintaining healthy levels of public debt, efficient financial markets and sound regulatory frameworks that can prevent or mitigate financial crises.
- Innovation and technology adoption: Economies that embrace innovation and technology can adapt more quickly to changing global trends and market demands. This includes investing in research and development and creating an enabling environment for new businesses and technological advances.
- Sustainable practices: Integrating sustainability into economic planning can reduce the long-term risks associated with environmental degradation and climate change. Sustainable practices not only protect the environment, but also create new economic opportunities in green technologies and industries.
Effective governance and policy-making: Resilient economies are underpinned by forward-looking and effective governance. This includes planning and implementing policies that anticipate future challenges, including demographic shifts, technological change and climate-related risks. - Social safety nets: Strong social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, health care and education, can help maintain social stability and consumer confidence during economic downturns, facilitating a faster recovery.
- Global cooperation: In an interconnected world, international cooperation and trade relations can play a crucial role in building economic resilience. This includes participating in global supply chains, adhering to international standards and engaging in global governance structures.
Conclusion – The management of policies for economic growth
All these policies have the potential to boost economic growth. However, they need to be carefully designed and implemented to be effective. As noted above, there are many short-term gains with potential long-term consequences that need to be taken into account when formulating economic policy. With many governments also implementing policies that have international implications, getting it right is becoming increasingly difficult. A current example is the devaluation of currencies by many central banks in an attempt to boost exports. As almost every central bank is trying to do this, it is a race to the bottom.
The most important thing is to have a clear understanding of the objectives of the economy, the effects of policy and, above all, the trade-offs. With this in mind, it is possible to design policies that help stimulate economic growth while protecting other important objectives such as economic stability and long-term growth.

Comments are closed.